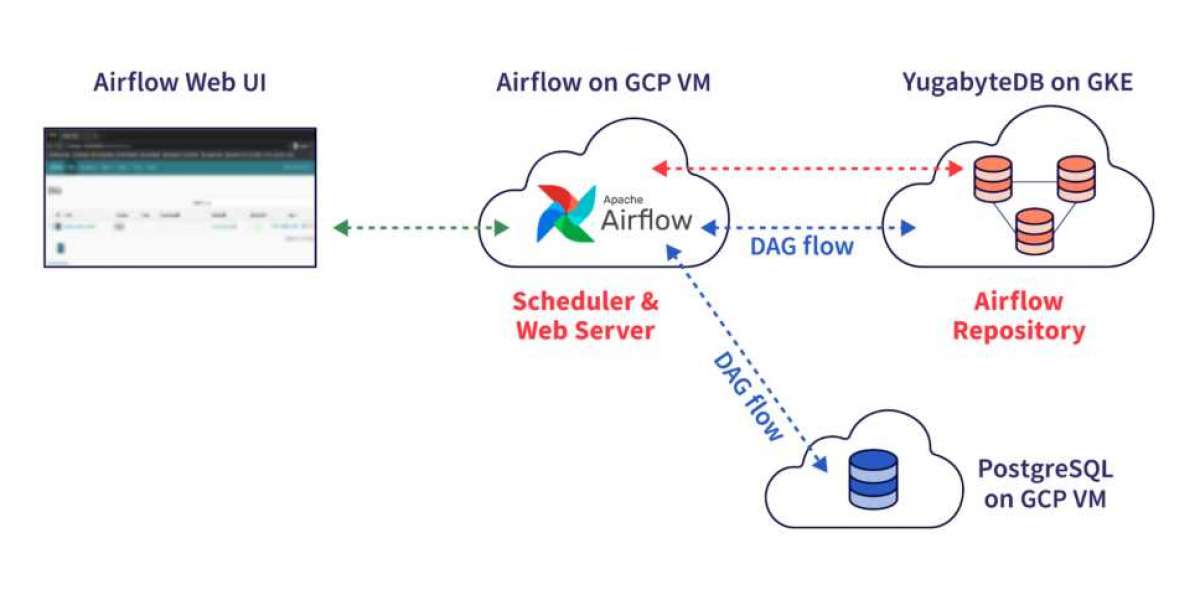
Welcome to the second part of our series on combining Apache Airflow and YugabyteDB. In our previous article, we walked you through setting up Airflow to work with YugabyteDB as a backend. Now, we'll show you how to create an Airflow workflow that transfers data between PostgreSQL and YugabyteDB.
What is YugabyteDB? It's an open-source, high-performance distributed SQL database built on a scalable and fault-tolerant design inspired by Google Spanner. Yugabyte's SQL API (YSQL) is compatible with PostgreSQL.
Migration Workflow Demo
In this article, we'll create a simple Airflow DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) that detects new records inserted into PostgreSQL and transfers them to YugabyteDB. In a future post, we'll explore more complex YugabyteDB workflows and DAGs.

We'll cover the following steps in this article:
- Setting up PostgreSQL
- Configuring GCP firewall rules
- Configuring Airflow database connections
- Creating an Airflow task file
- Running the task
- Monitoring and verifying the results
Getting Started
Below is the environment we'll be using for this blog post.
- YugabyteDB – version 2.1.6
- Apache Airflow – version 1.10.10
- PostgreSQL – version 10.12
- A Google Cloud Platform account
Note: For the purposes of this demo, we're focusing on demonstrating how to set everything up with minimal complexity. In a production deployment, you'll want to implement additional security measures throughout the stack. For more information on migrating PostgreSQL data to distributed SQL in minutes with Apache Airflow, visit t8tech.