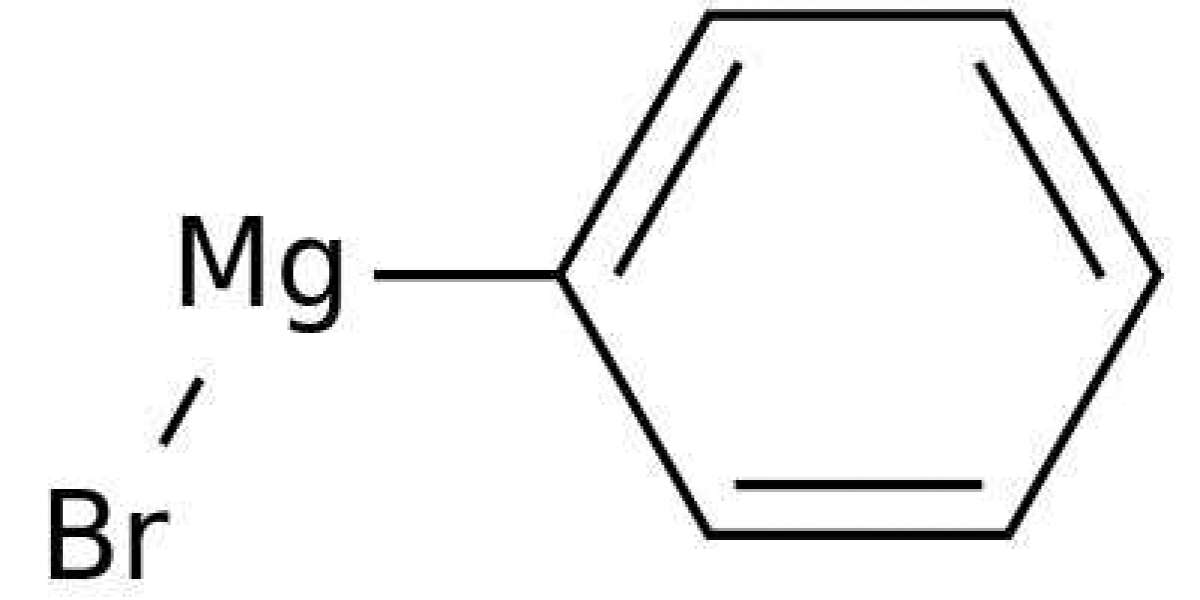
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Diphenylprolinol (also known as diphenyl-2-pyrrolidinylmethanol, D2PM, α,α-diphenyl-2-pyrrolidinemethanol, and GPI-2089) and 2-(diphenylmethyl)pyrrolidine (also known as desoxy-D2PM, 2-benzhydrylpyrrolidine) are the pyrrolidine analogues of pipradrol and desoxypipradrol, respectively. A detailed review of the methods of synthesis for 2-(diphenylmethyl)pyrrolidine and diphenylprolinol was published on the former Rhodium website and is currently archived on the Erowid website. Diphenylprolinol was first synthesised in 1933 from proline ethyl ester by reaction with phenylmagnesium bromide. However, it was not until 1961, when racemic diphenylprolinol was synthesised using this method for potential clinical applications, that this compound was shown to have central stimulant activity when administered parentally to rats. A few years later, the reduction of diphenylprolinol using hydriodic acid was reported in the patent literature for the production of (S)-2-diphenylmethylpyrrolidine as a potential central stimulant.
Interestingly, pipradrol, diphenylprolinol and 2-(diphenylmethyl)pyrrolidine later found use as chiral organic catalysts, which subsequently led to an explosion of research on organocatalysts. Kanth reported a convenient synthesis of diphenylprolinol from (S)-proline using ethyl chloroformate to simultaneously produce the (S)-proline ethyl ester with an N-protecting group. This intermediate was then reacted with phenylmagnesium bromide to produce a cyclic carbamate which was then hydrolyzed with potassium hydroxide. A nitrogen-protecting group has also been utilised for the synthesis of diphenylprolinol from pyrrolidine and benzophenone. The chiral properties of 2-(diphenylmethyl)pyrrolidine have also been exploited in analytical chemistry as a chiral solvating agent for the determination of enantiomeric composition of chiral carboxylic acids by NMR analysis. For this application, Bailey modified the method of Kanth by hydrogenating the cyclic carbamate to produce 2-diphenylmethylpyrrolidine.
Before defining the scope of this chapter and providing discussion of the chemistry of organocopper compounds, a short historical overview should be presented. After Viktor Grignard was awarded the Nobel prize in 1912 for his seminal contributions to organomagnesium compounds, several researchers became interested in the preparation of organometallic species and as pointed out above, the first organocopper compound was described in 1923 by Reich. Reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide with copper iodide gave phenyl copper and this disclosure proved the existence of such organometallic species. Within the next few years, several new copper compounds were described and in 1936, Gilman and Straley reported the preparation of ethylcopper as the first monoalkylcopper compound. The authors were further able to show the intrinsic difference of organocopper species to Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds.